TUAREG CROSS OF AGADEZ 4

Map of the Sahara desert
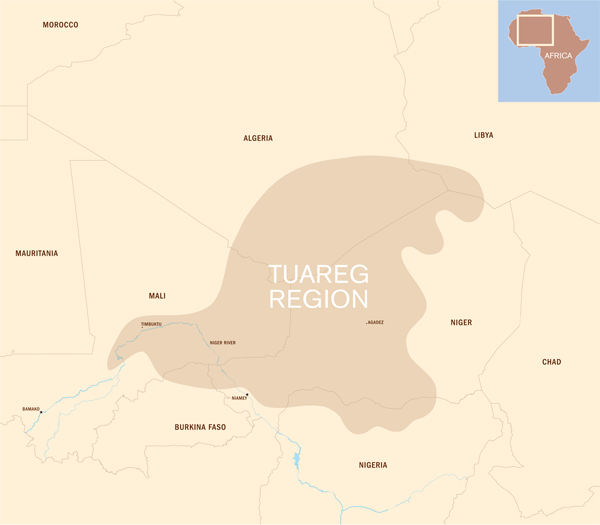
The traditional distribution of the Tuareg in the Sahara. Smithsonian Institution, USA.

Tuareg Silver and the Material Culture of Memory
Abdulrahman Bashir, Mustafa Abdullah. 2022. “The Tuareg: Literature, Language, and Culture.” Sada Online Journal, December.
– Overview of Tuareg cultural identity and oral traditions.
Aghali-Zakara, M. 1993. Bijoux touaregs du Niger: Symbolique et fabrication traditionnelle. Niamey: Centre Culturel Franco-Nigérien / Mission Culturelle Nigérienne.
– Foundational fieldwork study on Tuareg jewelry symbolism and silversmithing traditions.
Al-Kauni, Ibrahim. 1997. Goldstaub. Basel.
– Literary interpretation of Tuareg metaphysics and desert imagery relevant to silver symbolism.
Arabic Lexicography. n.d. Hans Wehr Dictionary of Modern Written Arabic; Lane’s Lexicon (Classical). Alhassanain.org.
– Encyclopedic linguistic references on bādiyah (steppe) and ṣaḥrāʾ (desert).
Attack of a French Convoy by Tuareg Tribe. 1925. Le Petit Journal, 18 January. Reprinted in Media Storehouse archives.
– Contemporary visual record of colonial encounters with Tuareg confederations.
Becker, Christina, and Barbara Nowak. 2022. “Iklan Aesthetics in Niger: Identity and Adornment from Servility to Self-Agency.” African Arts 55: 10–25.
– Examines adornment and self-representation among formerly servile Tuareg groups.
Beltrami, Vanni. 1994. “Croix d’Agadez.” Encyclopédie berbère 14: 2129–2133.
– Authoritative reference on Tuareg cross typologies and regional variations.
Bernus, Edmond. 1981. Touaregs nigériens: Unité culturelle et diversité régionale. Paris: ORSTOM.
– Classic anthropological synthesis of Tuareg social organization and artisanal production.
Bernus, Edmond, and Johannes Nicolaisen. n.d. Structures politiques et sociales des Touaregs de l’Aïr et de l’Ahaggar. Paris: Horizon Documentation.
– On the sociopolitical organization of Tuareg confederations.
Bernus, Edmond, Pierre Boilley, Jacques Clauzel, and Jean-Louis Triaud, eds. 1991. Nomades et commandants: Administration coloniale et sociétés nomades dans l’ancienne A.O.F. Paris: Horizon Documentation.
– Key volume on colonial governance and nomadic societies.
Bernus, Suzanne, and Edmond Bernus. 1988. Artisanat touareg. Paris: Éditions Recherches sur les Civilisations.
– Detailed study of Tuareg crafts, including smithing and jewelry.
Boffa, Ada. 2024. “La Croce di Agadez, simbolo del mondo tuareg e saheliano.” Dialoghi Mediterranei 66: 1–7.
– Contemporary overview of the Agadez cross as a symbol of Sahelian identity.
Borel, France, and Jean-Marie Glas. 1984. Argent du désert: Bijoux touaregs du Niger. Paris: Adam Biro.
– Exhibition catalogue with ethnographic commentary and extensive photographic documentation.
Bradshaw Foundation. 2022. “The Tuareg Salt Caravans of the Sahara.”
– Educational feature on salt-silver exchange routes.
Brett, Michael. 1985. “Trade and Travel in the Sahara.” The Journal of African History 26(2): 255–278.
– Historical analysis of trans-Saharan trade and the economic role of silver.
Claudot-Hawad, Hélène. 1986. “La conquête du ‘vide’: essais sur la désertification de l’imaginaire.” Cahiers de l’Institut d’Anthropologie Sociale (OpenEdition).
– Philosophical reflection on the desert as symbolic space.
———. 1993. Touaregs: Portrait en fragments. Aix-en-Provence: Édisud.
– Influential essays on Inadan smiths, hierarchy, and the symbolic value of metalwork.
———. 1996. “Le territoire-chemin: circulation et droit du sol chez les Touareg.” Revue du Monde Musulman et de la Méditerranée 79: 87–108.
– Seminal study on Tuareg territoriality and mobility.
———. 2010. “Figures of Alterity among the Tuareg: The Inadan Artisans and the Logic of Marginality.” Journal des Africanistes 80(2): 43–65.
– On the paradoxical role of smiths as marginal yet central cultural mediators.
———. 2021. “From Camel to Hashtag: Tuareg Silver in the Attention Economy.” Journal of Material Culture 26(3): 287–306.
– Interprets Tuareg silver in the context of globalization and digital visibility.
———. n.d. “Nomadisme chez les Touaregs.” Encyclopédie berbère (OpenEdition).
– Overview of nomadic structures and desert itineraries.
———. n.d. “The Sociopolitical Organisation of a Nomadic Society (Tuaregs).” Nomadsed.de.
– Discusses lineage systems and colonial reinterpretations of leadership.
Colonial Conquest and Statecraft in the Niger Bend, c. 1893–1936. 2025. In A History of Race in Muslim West Africa, 1600–1960. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
– Contextualizes French colonial policies affecting Tuareg confederations.
Dieterlen, Germaine, and Ziedonis Ligers. 1972. “Contribution à l’étude des bijoux touareg.” Journal des Africanistes 42(1): 29–53.
– Foundational typological study of Tuareg jewelry and amuletic symbology.
Fondazione Slow Food. n.d. “Taoudenni Salt – Ark of Taste.”
– Documentation on Saharan salt heritage linked to silver trade routes.
Fowler, Ian, and Rebecca F. S., eds. 2005. African Crossroads: Intersections Between History and Anthropology in the Great Sahara. Oxford: Berghahn.
– Essays on trade, metallurgy, and cultural symbolism of exchange.
Gabus, Jean. 1982. Sahara: Bijoux et techniques. Neuchâtel: Musée d’Ethnographie.
– Museum-based ethnography of Saharan jewelry techniques and iconography.
Göttler, Gerhard. 1989. Die Tuareg: Kulturelle Einheit und regionale Vielfalt eines Hirtenvolkes. Cologne.
– Study of Tuareg cultural unity and regional diversity, including crafts.
Gouletquer, Philippe. 1984. Bijoux et amulettes touaregs. Paris: Musée de l’Homme.
– Catalogue of Tuareg jewelry and tcherot amulets.
Hahn, Hans Peter. 2014. Materielle Kultur: Eine Einführung. Berlin: Reimer Verlag.
– Theoretical framework on material culture and memory.
Heath, Jeffrey. 2005. A Grammar of Tamashek (Tuareg of Mali). Berlin: Mouton de Gruyter.
– Authoritative linguistic description of Tamasheq grammar and lexicon.
Lecocq, Jean-Sébastien (Baz). 2010. Disputed Desert: Decolonisation, Competing Nationalisms and Tuareg Rebellions in Northern Mali. Leiden: Brill / Universiteit Leiden.
– Major historical reference on Tuareg rebellions and postcolonial identity.
Loughran, Kristyne. 2003. “Jewelry, Fashion, and Identity: The Tuareg Example.” African Arts 36(3).
– On jewelry as gendered and cultural self-expression.
Maïga, Aïcha, and Abdou Harouna. 2024. “Artistic Expressions in Tuareg Jewelry of Niger: Design, Craftsmanship, and Cultural Significance.” Art and Society (June 2024). https://doi.org/10.56397/as.2024.06.07
Masquelier, Adeline. 1997. Prayer Has Spoiled Everything: Possession, Power, and Identity in an Islamic Town of Niger. Durham: Duke University Press.
– Examines purity and value metaphors (silver vs. gold) in Sahelian Islam.
Nicolaisen, Johannes, and Ida Nicolaisen. 1997. The Pastoral Tuareg: Ecology, Culture, and Society. Copenhagen: National Museum of Denmark.
– Monumental ethnography on Tuareg institutions and craftsmanship.
Ornament Magazine. 2018. “Tuareg Jewelry: Traditions in Transition.” Ornament 41(3).
– Article on adaptation and design evolution in Tuareg silver.
Prasse, Karl-G. 1990. Manual of Berber Phonology. Hamburg: Buske Verlag.
– Linguistic reference on Berber phonetics relevant to Tamasheq.
———, et al. n.d. Dictionnaire touareg-français (Niger). Open-access via Internet Archive.
– Standard lexicon for Tamasheq vocabulary including tiniri / ténéré.
Rasmussen, Susan J. 1995. Spirit Possession and Personhood among the Kel Ewey Tuareg. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
– Ethnographic study of ritual adornment and women’s agency.
———. 2008. “The People of Solitude: Recalling and Reinventing Essuf in Tuareg Space.” Journal of the Royal Anthropological Institute 14(3): 609–627.
– Explores essuf (solitude) and material symbols in desert life.
———. 2012a. Cultural Resilience and Identity in the Tuareg Artisan Community. Urbana: University of Illinois Press.
– Contemporary ethnography on craft cooperatives and adaptation.
———. 2012b. “Neighbors, Strangers, Witches, and Culture-Heroes: Ritual and Social Aesthetic Understandings of Blacksmith/Artisans in Tuareg Society.” Ethnology 49(3): 185–206.
– On the symbolic aesthetics of the Inadan.
———. 2012c. “Frontiers of Memory: Trauma and Territory among Tuareg Refugees.” Cultural Anthropology 27(1): 33–55.
– Discusses memory and displacement among Tuareg artisans.
———. 2020. “Images of Loneliness in Tuareg Narratives of Travel and Return.” Anthropology & Humanism 45(2): 170–186.
– Interprets travel and solitude in contemporary Tuareg storytelling.
Rodd, Rennell. 1926. People of the Veil. London: Macmillan.
– Early colonial account documenting Tuareg metalwork and social customs.
Rossi, Benedetta. 2021. “Entangled Histories of Colonial Occupation, 1899–1917.” In Colonial Echoes in West African Borderlands. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
———. n.d. “On Slavery and Servitude Trajectories in the Sahel — Legal Abolition vs. Social Continuity.” Benedettarossi.com.
– Analyses of colonial governance and post-abolition servitude among Tuareg and neighboring groups.
Seligman, Thomas K., and Kristin Loughran, eds. 2006. Art of Being Tuareg: Sahara Nomads in a Modern World. Los Angeles: Fowler Museum, UCLA.
– Landmark exhibition catalogue on Tuareg art, metalwork, and contemporary identity.
Sotkiewicz, Hanna. 2023. “Amulets and Talismans of the Central Sahara — Tuareg Art in Context of Magical and Mystical Beliefs.” Wolfgang Goethe University Frankfurt.
– Academic study of Tuareg amulets and protective symbolism.
Spittler, Gerd. 1998. Handwerk in Afrika: Zur materiellen Kultur der Tuareg und anderer Gesellschaften. Köln: Rüdiger Köppe Verlag.
– Comparative ethnology of African crafts with focus on Tuareg Inadan.
Spurlock Museum Blog. 2019. “Beauty and Adornment: Tuareg Jewelry.” University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign.
– Museum commentary on aesthetics and symbolism.
Sudlow, Jill. 1998. Tuareg Jewelry: Traditional Patterns and Modern Adaptations. London: Thames & Hudson.
– Illustrated monograph linking traditional symbolism to modern design.
Tuareg Nationalism and Cyclical Pattern of Rebellions. 2012. Research Report, University of Florida.
– Political analysis of Tuareg movements and socio-economic shifts.
Wikipedia. n.d. Entries on “Battle of Tit (1902),” “Territoires du Sud,” and “Kaocen Revolt (1916–17).”
– Basic historical anchors (to be cross-checked with primary sources).
Zeltner, Jean-Claude. 2000. Le sel et l’argent: Échanges transsahariens et cultures du désert. Paris: CNRS Éditions.
– Interdisciplinary study of the symbolic and economic interplay between salt and silver in Saharan trade.

Alyx Becerra
OUR SERVICES
DO YOU NEED ANY HELP?
Did you inherit from your aunt a tribal mask, a stool, a vase, a rug, an ethnic item you don’t know what it is?
Did you find in a trunk an ethnic mysterious item you don’t even know how to describe?
Would you like to know if it’s worth something or is a worthless souvenir?
Would you like to know what it is exactly and if / how / where you might sell it?
